Yesterday (2020-9-28), Ms. Liu, a reporter from the Taiwan Affairs Inspection Center, sent an email saying that they were checking a message about "vitamin C can prevent active detachment", so I hope to visit me.
"Operational Death" is a popular topic in Taiwan's media in the past six months, and this is because only 36-year-old artist Huang Dongsheng died suddenly on September 16, 2020 due to active death.
In fact, a few days ago (2020-9-24) reader George Hsu used the website's "Contact Me" to ask me "Is vitamin C able to repair the structure of the zodiac, is it true? 》, and the online link he attached was to lead an article saying "Vitamin C can prevent active dysfunction."
This article was published on the face book by natureist Chen Junxu on September 19, 2020. The title is how to prevent active stamina? . I copied several of its key points as follows:
1. The problem is that the lint is fragile, and to put it bluntly, it is insufficient vitamin C intake.2. Regardless of the cause, prevention, or maintenance, a large amount of vitamin C and gelatin peptide should be supplemented to strengthen the inner tissue to prevent it from rupturing.
3. The entire treatment direction is to strengthen the lint organization, especially the supplementation of vitamin C and bio-keto. Eating fruits and vegetables is far away and requires a large dose.
4. Repairing the titanium is a very important thing, it involves at least one hundred diseases. It depends on vitamin C, but pharmaceutical manufacturers do not like vitamin C because if this disease is so easy to treat, everyone will not take medicine!
Therefore, Chen Junxu's natural saurus believes that the prevention and treatment of active stasis is actually very simple, that is, vitamin C needs to be supplemented with large doses.
Although I knew from the bottom of my heart that this was ridiculous, I still did a lot of checks seriously for fairness. First, I went to the public medical library PubMed to search with the two keywords "vitamin C and aortic dissection" and the result was zero. Then I also searched on a website of the Linus Pauling Institute website that specialized in Vitamin C, and the results were also zero.
Linus Pauling Institute was founded by Dr. Linus Pauling in 1973, and its most important task is to prove that vitamin C can prevent and treat various diseases. In other words, it is unlikely that anyone or organization in this world would want to prove (or even if it is just a sound) that Vitamin C can prevent or treat active detachment more than Linus Pauling Institute. But why doesn't it mention it?
{twenty three} {twenty four}
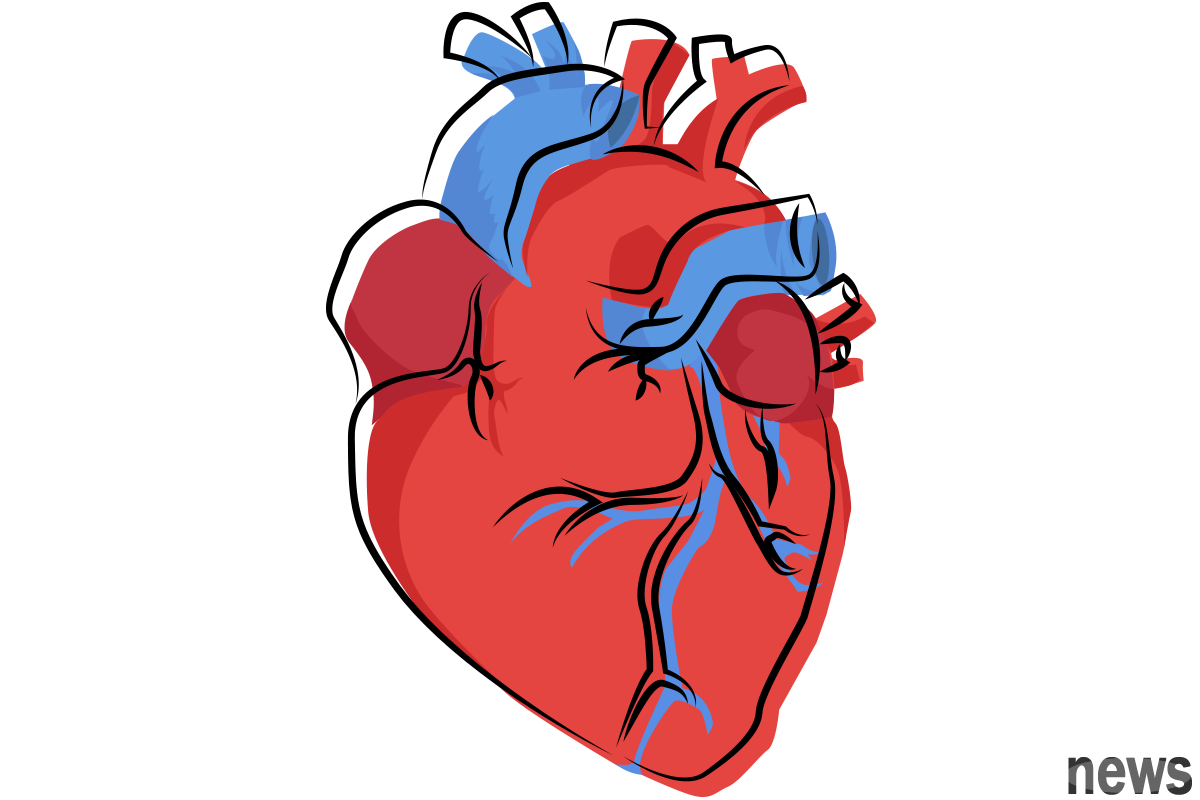
All large veins, including active veins, have three layers of structure, namely endothelium (also called tunica intima), smooth muscle (also called tunica media), and tunica adventitia.
Under normal circumstances, blood flows in the blood vessels and only contacts the endothelial layer. If the blood in the active vent penetrates the endothelial layer and flows into the smooth muscle layer, it will cause tearing of the endothelial layer and the smooth muscle layer. This phenomenon is called aortic dissection.
The reason why active venting occurs is simply that when the blood pressure is higher than the limit that the active duct wall can withstand, the blood will penetrate the endothelial layer, resulting in tearing of the endothelial layer and smooth muscle layer. This is why people suffering from hypertension are high-risk groups that actively depart. However, most people with hypertension will not experience active dysfunction, so this means that there must be other factors that will trigger active dysfunction.
As mentioned in the previous paragraph, the reason why active vent stagnation occurs is because the blood pressure is higher than the limit that the active calcification wall can withstand, so the quality of the active calcification wall is another important factor in whether active calcification will occur.
The quality of the active tube wall is determined by the extracellular matrix. However, since most people don’t understand what Extracellular Matrix is, it is often referred to as “End Organization”, although Entangle Groups actually include hard bones, soft bones, fat, blood, etc. and are not extracellular Matrix. The main member of
extracellular matrix is collagen, while the other one with a smaller quantity, but is also indispensable is elastic protein (elastin). In terms of active veins, the fiber formed by the gel protein is responsible for the tensile strength of the active veins, while the fiber formed by the elastic protein is responsible for the expansion and recoil properties of the active veins. Therefore, when the standards formed by these two proteins are well matched, the texture of the active tube wall will be better. On the contrary, when the fibers formed by these two proteins are not well matched, the texture of the active tube wall will be bad..
gelatin synthesis requires vitamin C, which is why Chen Junxu naturalist believes that supplementing vitamin C with large doses can prevent and treat active dysfunction. However, as mentioned in the previous paragraph, in addition to gelatin, the structure and function of active lesion also requires elastic proteins. Unfortunately, although vitamin C promotes the synthesis of gelatin protein, it inhibits the synthesis of elastic proteins. See Ascorbate differently regulates elastin and collagen biosynthesis in vascular smooth muscle cells and skin fiberbroblasts by pretranslational mechanisms.
Also, studies have found that too much gelatin increases stiffness of the veins, which may lead to active veins, while too little gelatin weakens the active wall, which may lead to active veins. That is to say, whether the gelatin is too much or too little, it may increase the risk of active dysfunction. See Extracellular matrix, regional heterogeneity of the aorta, and aortic aneurysm.
In summary, supplementing vitamin C with large doses may cause an imbalance in the ratio between gelatin and elastic protein, and on the other hand, it may also increase the stiffness of the veins, and both of these situations will increase the risk of active veins. However, these are just reasoning based on the evidence from the laboratory. There is no clinical evidence that large dose supplementation of vitamin C can cause active dysfunction or increase its risk.
Original text: Vitamin C prevents active voluntary nonsense